









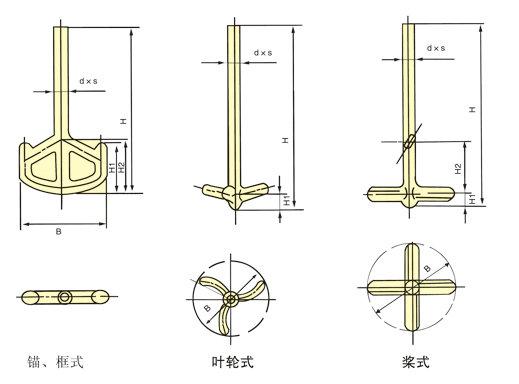
The frame stirrer is generally used for mixing Congee like materials. The proper mixing speed is 60-130 r/min. It usually operates at a low speed and does not produce large shear force when mixing low viscosity liquids. Therefore, it is not suitable for liquid-liquid and gas-liquid dispersion.
The impeller of the frame mixer moves at a high flow rate inside the tank, with horizontal rotational flow dominating and lacking good mixing uniformity. However, the flow velocity near the tank wall can achieve a higher heat transfer film coefficient than other impellers, making it commonly used for heat transfer and crystallization operations. In addition, due to the large diameter of the blade and its proximity to the bottom of the tank, it is also commonly used to stir high concentration slurries and precipitating slurries. It is also commonly used for stirring high viscosity fluids. Choosing the appropriate stirrer based on the physical properties, capacity, and stirring purpose of different media can play a significant role in promoting chemical reaction rates and improving production efficiency.
It can be regarded as a deformation of the paddle mixer, which has a relatively sturdy structure and a large amount of animal material to be stirred. If the shape of the bottom of such a stirrer is similar to the shape of the lower head of the reaction vessel, it is usually called an anchor stirrer. The diameter of the frame stirrer is relatively large, usually taking 2/3-9/10 of the inner diameter of the reactor, and 50-70r/min. The gap between the frame stirrer and the reactor wall is small, which is conducive to the heat transfer process. When rotating rapidly, the liquid driven by the stirrer blades brings the stationary layer down from the reactor wall; When rotating slowly, a stirrer with a scraper can generate good heat conduction. This type of agitator is commonly used for heat transfer, crystallization operations, and stirring of high viscosity liquids, high concentration slurries, and settling slurries.

 Address:Room 1202, Detaitang Building, No. 118 Huaguang Road, Zhangdian District, Zibo, Shandong
Address:Room 1202, Detaitang Building, No. 118 Huaguang Road, Zhangdian District, Zibo, Shandong WhatsApp:+8613386433135
WhatsApp:+8613386433135 Tel: +8613386433135
Tel: +8613386433135